Sodium chloride, or salt, is found naturally in water.
As an essential element, salt is crucial for your health: it maintains optimum blood pressure levels and assists with nerve and muscle function.

But too much of anything is usually bad for you.
So, how do you remove salt from water?
I intend to explain that in this article, but first, let’s discuss how salt can get into drinking water.
How Does Salt Get Into Drinking Water?
Sodium chloride is a naturally occurring element in seawater, surface water, and groundwater.
Surface water is just that: water that can be obtained from rivers, lakes, ponds, and the sea.
Groundwater is water that soaks into the soil and is held in aquifers (1): impenetrable rock layers or sediment enclosing water deposits.
What Are Safe Levels of Sodium In Drinking Water?
Remember that sodium and sodium chloride is not the same thing (2): salt comprises sodium, which is a mineral, and chlorine, which is a chemical element.
When these two substances bond, they form NaCl, or sodium chloride.
So when your doctor advises you to reduce your salt intake, they mean you are taking too much sodium.

You know you’ve added too much salt to your food because you can taste it — the chlorine that gives it that salty flavor.
There is no mandated level of sodium in drinking water in the U.S., but the recommended dose is between 20mg/L (milligrams per liter) and 270mg/L, depending on your health status.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) states (3) that we imbibe about 3,400mg of sodium daily from our food.
The recommended daily intake is about 1 teaspoon or less than 2,300mg.
What Are The Effects Of Sodium In Soft Water?
Hard water has high mineral content.
To soften water, minerals such as magnesium and calcium are removed, and small amounts of sodium are added through an ion exchange process.
Soft water will therefore contain higher sodium levels, but this does not necessarily equate to unhealthy levels.
Recommended Reading: How to Make Hard Water Soft? + (Effective Methods)
Showering or bathing in soft water differs from using hard water: the more dissolved soap there is, the more needs to be rinsed off.
It’s easy to use more soap or detergent than you need, as it lathers more easily in soft water, which then needs more rinsing.
How Do You Remove Sodium From Softened Water?
We have established that soft water has a higher sodium content than hard water.
Softened water using the ion exchange process would have had sodium added.
If you prefer not to use softened water, there are ways to get rid of sodium:
Recommended Reading: Chlorine in Drinking Water : (5 Clever Ways to Test & Remove) & Is Softener Salt Safe to Eat?
Potassium Chloride
Potassium chloride can be used instead of sodium to soften water. This is what I use…
- This Product is strictly intended for business, commercial, and industrial use. Customers must have a comprehensive understanding of each product’s intended use. Potassium Chloride FCC is 99% salt of potassium with max. 1% magnesium hydroxide carbonate that meets Food Chemical Codex standards.
- For the manufacture of dietetic salts, as salt substitute, finishing of carrageenan products and other food and food additive uses. Also for production of other potassium compounds for human consumption. Our production is IFS 6 Food certified
- Potassium Chloride FCC is a white crystal with a slight salt taste.
- Storage: Keep the closed original packaging at a dry and cool place (preferably 5 - 30 °C) without direct exposure to sunlight.
- Chemical Name: Potassium chloride, magnesium hydroxide carbonate
It uses the same process, i.e., it replaces hard minerals such as calcium and magnesium with potassium rather than sodium.

It is a more expensive solution as mining potassium chloride is costlier than mining sodium chloride.
Potassium chloride is also essential to the healthy growth of both plant and animal life, including humans.
Adding potassium chloride to water has been proven to remove up to 90% of the sodium present.
Reverse Osmosis
The most effective method of neutralizing salt content from water is reverse osmosis.
Reverse osmosis works by forcing water through a semipermeable membrane under high pressure.
The holes in the membrane allow the passage of hydrogen and oxygen, which water is composed of — H2O.
I have used and installed many RO systems over the years and the one I turn to most often is from SpringWell.
Most other molecules are too large to pass through the membrane, including sodium and chlorine which make up salt.
RO also removes up to 95% of other minerals such as magnesium, iron, lead, fluoride, copper, chlorine, and many others.
Electrodialysis
The process of Electrodialysis Reversal Salination (EDR) works by running an electrical current through conductors or electrodes.

This extracts the dissolved salts in water by straining them through an ion-exchange membrane.
This results in the water being separated into two channels: one with a high sodium content and one with low sodium content.
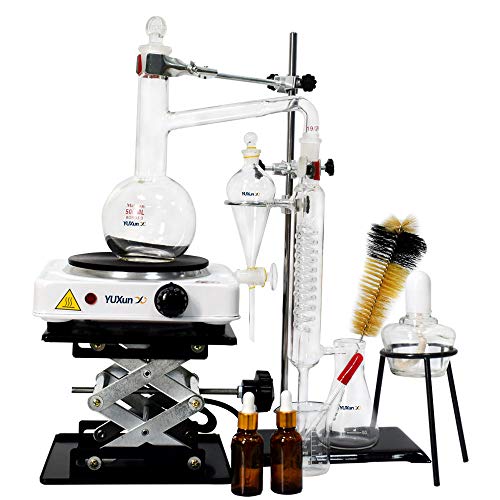
Distillation
Distillation entails boiling liquid that evaporates, turning it into a vapor.
This is passed through a series of pipes at low temperatures to cool it, condensing the vapor.
The vapor then reverts to water, called the distillate.
This is a good unit for home use:
- Note: The lift table is not included in the package, It needs to be purchased separately. SUPERB QUALITY - All glassware are made of upgraded 3.3 Borosilicate Thicken Glass material, hand blown and polished for perfect fit. Joints are all standard size. Include a metal stand with clamps to tightly fix the devices.
- PROFESSIONAL KIT - Consist of: Flat Flasks, stand, clamps, joints, silicone hose, condenser, receiver/separatory funnel, glass stopper, electric Hot Burner, which can meet all your needs. Good sealing, no leakage of water or steam with glass stopper.
- DIVERSE APPLICATION - Perfect to use for essential oil, hydrolat extraction, distilled water collection at lab, home, research center, teaching etc. High distillation rate, save your money and can DIY any essential oil you like.
- Perfect set for organic chemistry labs, distillation, fractional distillation, separation, purification, and synthesis. Can be used as experimental teaching equipment, alcohol, essential oil distillation.
- 100% Satisfied Service Professional customer service.One Year With Free Replacement.Please don't worry, we will pack the product strictly,the damage rate of the package will be less than 2%.
The salts and minerals in the water are left behind, purifying the distillate.
Other substances (4) besides water can be distilled, such as alcohol, paraffin, and kerosene, and are also used in gasoline production.
Gases such as argon, oxygen, and nitrogen can be distilled from the air.
How Is Salt Removed From Sea Water?

We are unable to drink seawater as the salt levels are too high for our kidneys to process.
Freshwater is needed to dilute the excess salt and produce urine, which rids your body of waste.
The saline content of seawater is about 35 parts per thousand (5), making it impossible for us to digest.

If you drink undiluted seawater, you will die of dehydration as the salt draws water out of your cells via osmosis.
The process of removing salt from seawater is called desalination.
Desalination removes salt and other minerals from seawater, brackish water, or other saline water sources to produce fresh drinking water.
While desalination is becoming increasingly important as populations grow and water resources become scarcer in some parts of the world, desalination can be energy-intensive and expensive. It may have environmental impacts, such as brine discharge, which can harm marine life. As such, desalination is often seen as a supplement to, rather than a replacement for, other water sources and conservation efforts.
Reverse osmosis is usually used to treat seawater. Still, the resulting wastewater, which contains concentrated salt, can be toxic to ocean plants and animals when returned to its source.
Natural distillation is another way to purify salt water.
The heat from the sun causes water to evaporate from expanses of water with large surface areas such as lakes and streams.
The resulting water vapor combines with cooler air which forms dew or rain.
The salt residue that is left behind in pans can be recovered and processed for human consumption.
Salt pans can occur naturally or be man-made.
Does Boiling Saltwater Remove Salt?

Although the amount of heat required to boil saltwater is less than for freshwater, boiling water will not remove its salt content.
The salt needs to be extracted by other methods as discussed above to make it fit for human or animal consumption.
The boiling point of sodium is 621o F, while the boiling point of water at sea level is 212o F.
Boiling water removes almost 100% of pathogens and contaminants, but not salt.
FAQ’s
How do you get salt out of tap water at home?
There are several ways to remove salt from tap water at home, including distillation, reverse osmosis, ion exchange, and freezing. Distillation involves boiling the water and collecting the steam in a separate container, while reverse osmosis involves forcing the water through a semi-permeable membrane. Ion exchange uses a resin that exchanges salt ions for hydrogen ions, while freezing involves removing the ice to leave behind the salt. It’s important to note that these methods may not completely remove all of the salt from the water and some may remove beneficial minerals.
Can You Freeze Water To Remove Salt?
Yes. Freezing tap water removes salt by allowing the water to freeze completely and then straining out the ice crystals and any separated salt. This method is not a reliable or efficient way of removing salt from water, and other methods, such as distillation, reverse osmosis, or ion exchange, may be more effective.
Can you neutralize salt water?
It is not possible to neutralize salt water in the traditional sense, as salt water is not an acid or a base. However, it is possible to remove the salt ions from salt water through desalination, reverse osmosis, distillation, ion exchange, or freezing.
How to treat salty borehole water?
This typically involves combining physical and chemical processes to remove the salt and other minerals from the water. First, reverse osmosis involves forcing the water through a semipermeable membrane to remove the salt, while distillation involves boiling the water and collecting the steam in a separate container. Finally, a water softener uses a resin that exchanges salt ions for sodium ions to remove the salt.
Conclusion
Water is becoming an increasingly limited commodity and we need to find economically viable ways of conserving our water resources.
Removing salt from existing bodies of water will be a way forward, but technology will have to be further developed to make this feasible on the massive scale that will be required.
For now, saltwater is best enjoyed at the seaside.




![Best Filtered Water Bottles of 2024– [Tested & Reviews] 13 Best Filtered Water Bottle](https://waterfiltercast.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/best-filtered-water-bottle.jpg)

![Best Electronic Water Descalers – [Alternative Water Softener Options] 15 Best Electronic Water Descaler](https://waterfiltercast.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/best-electronic-water-descaler.jpg)